How Does a Coat Keep You Warm Physics
In addition the fur your fur coat is made of diverts the air. This ability to keep heat in is what keeps us warm.

Transcultural Nursing Theory Mid Nursing Theory Nursing Education Nursing Philosophy
The fibers have a natural crimp that helps to wick moisture away from the body.
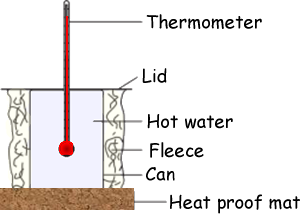
. Slip On A Vest. But generally your body keeps you warm by burning fats and the jacket provides insulation that stops you losing the warmth to the environment. You can keep the glass jars longer in the fridge and measure their temperature every 15 to 30 minutes.
However in keeping warm what is important is the radiation and conduction exchange with the environment. The real secret to staying warm is a measure of dead air or the pockets of gas within our coats or mittens that are too small to give rise to convection currents but still present as to slow conduction. So lets just take a look at the basic physics of how a warm object -- like a planet -- stays as warm as it does in a cold environment like interstellar space.
Fur holds body heat in much better than other types of winter coats. Cold is transferred from one object to another. Students will be able to explain that wearing a coat helps keep you warm because it blocks your bodys heat from moving away from you to where its cold.
But there are some other more complex elements to the wool fiber that. Well you can get electrically heated jackets for snowmobiles and motorcycles. Home insulation like styrofoam panels fibreglass or blown-in cellulose act like clothing in reducing heat transmission by convection.
Your coat slows this heat exchange down so that your body can produce heat faster than it emits heat to the surroundings. In fact black clothing is the best way to. You want that heat from burning food to be able to flow out so you dont heat up but not flow out too quickly.
Help with GCSE Physics AQA syllabus A AS Level and A2 Level physics. Why You Should Stock up on Organic Linen. In less comfortable thermal environments clothes can make a much larger difference.
Objects that keep things warm sweaters mittens blankets are sources of heat. There can still be conductive cooling through the cloth but cloth is a good insulatorHome insulation like styrofoam panels fibreglass or blown-in cellulose act like clothing in reducing heat transmission by convection. This effect improves the coats insulation potential.
As your body creates heat it is prone to letting that heat loose which ends in your feeling colder faster. Coats help keep us warm due to the fillings inside the materials. In the winter we normally wear coats.
A coat helps slow down the flow of heat out to the air so it helps on cold days. There can still be conductive cooling through the cloth but cloth is a good insulator. However if the threshold were lowered between your body temperature than you could begin to overheat.
Take your traditional style and add some layers underneath to keep you as warm as possible underneath your coat. To do this the air has to move from your body through your down jacket this is using conduction because the air is moving through the tiny feathers that are in contact with each other. 1 Stop air moving.
Down feathers trap air molecules in tiny insulating pockets. The chemistry in your body is tuned to work best at your regular body temperature so its not good to cool down too much. Wearing a coat would lower the heat threshold for maintaining a healthy body temperature.
Our body supplies the heat and the material helps to trap body heat and keeps the heat from. 1 Convection air moving 2 Conduction touching 3 Radiation. It can do this by enclosing you like a plastic bag but more practically it can be fuzzy.
Fleece and cotton are two examples. An ideal super-blanket will address all three. The heat radiated and conducted from the environment would balance that lost by the body if it were at the environmental temperature here about 20 C.
Its the measure of these microscopic packets of air that allow our clothes to be warm without being unnecessarily expensive. From Real World Physics Problems How Animals Stay Warm with Blubber from Scientific American. Were all encouraged to wear white in summer since white clothing is supposed to keep us cool but it doesnt.
This is a thermogram of a man woman and child not wearing clothes. Heat is transferred from one object to another. Clothing especially wool traps air in small pockets which reduces or eliminates convection.
The more air space in a material otherwise known as loftiness or puffiness the warmer it will be. Heat and cold can be thought of as opposite ends of a continuum. Or strictly speaking the jacket traps still air.
If you overheat your body begins burning more calories as it attempts to lower your body temperature by for example sweating. Fuzziness makes lots of little difficult to move air pockets. Heat energy is lost from the human body.
The coat keeps the body heat in. Down Coats- Down jackets keep us warm by insulating the air that radiates from our bodies. Heat moves from the warmer object to the cooler object.
Clothing especially wool traps air in small pockets which reduces or eliminates convection. However there are ways that these losses can be reduced. Getting this moisture off your bare skin is a key element to keeping warm in wet conditions.
This takes winter layering to a whole new level. The coat isnt actually warm its your body thats warm. Physics revision site - recommended to teachers as a resource by AQA OCR and Edexcel examination boards - also recommended by BBC Bytesize - winner of the IOP Web Awards - 2010 - Cyberphysics - a physics revision aide for students at KS3 SATs KS4 GCSE and KS5 A and AS level.
The white and red. The coat keeps your bodys heat from moving away from you to where the temperature is colder. Objects keep things warm by trapping heat.
This is what fur is innately designed to do. Coats keep us warm because of the material of the coat. This material which is either down or fibers of polyester keeps the warmth from your body in these pockets thus preventing you from losing heat.
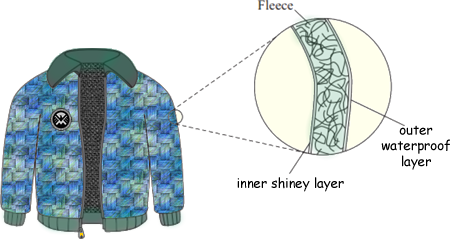
Physics Revision Gcse And A Level Physics Revision Cyberphysics The Revision Website

Physics Revision Gcse And A Level Physics Revision Cyberphysics The Revision Website
Comments
Post a Comment